Online video entertainment has created a huge impact to traditional media companies that didn’t believe in the huge opportunities that video-on-demand services where going to bring. They refused to acknowledge the market opportunities beyond traditional pay-TV services. This change has become a global phenomenon. The impact and implications are enormous.
But, what are Over-the-top services? Over-the-top, or OTT, is the term used for the delivery of film and TV content via the Internet, without requiring users to subscribe to a traditional cable or satellite pay-TV service like a Comcast or Time Warner Cable. OTT can be divided into three different revenue models:
- SVOD: Subscription-based model, such as the well-known Netflix or Hulu
- AVOD: Free and Ad-based services such as Cracked and Hulu
- TVOD: Transactional services such as Itunes
SVOD will become the region’s largest OTT revenue source in 2018. AVOD is expected to surpass SVOD in 2020, due to the rapid expansion in mobile advertising.
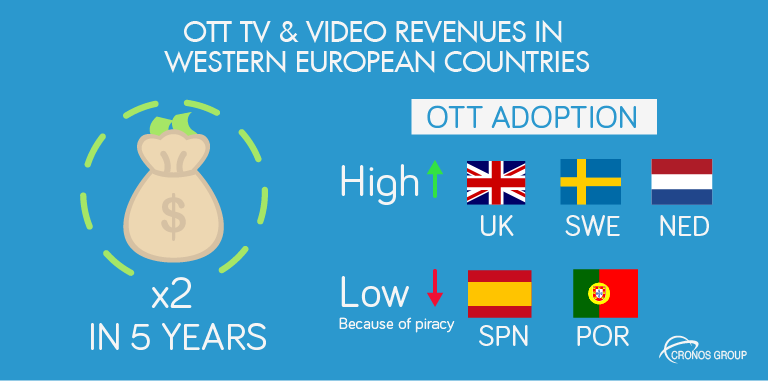
In Western European countries, over-the-top (OTT) television and video revenues will more than double in the 5 coming years. This growth rates will vary a lot, depending on the country. OTT adoption is high in UK, the Netherlands and specially Sweden, were in the south (Spain, Portugal) it hasn’t make a difference, yet. This is mainly because these countries report a huge presence of piracy content.
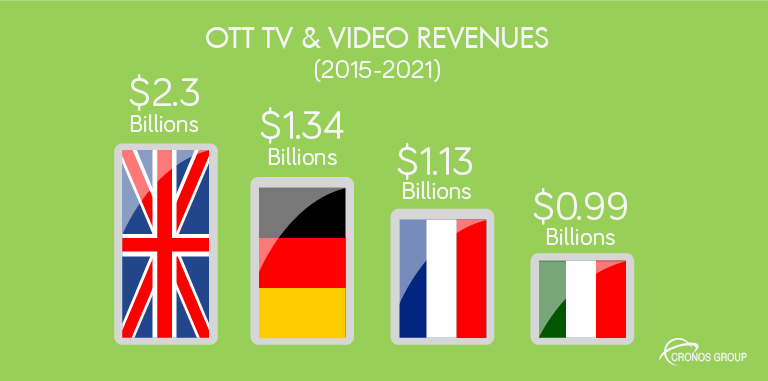
OTT TV and video revenues in Western Europe will be increased, between 2015 and 2021, in $8.25 billion. The UK will be the marked leader, with $2.30 billion, followed by Germany ($1.34 billion), France ($1.13 billion) and Italy ($0.99 billion)
However, growth will be tied to distribution. As internet-connected TVs become more and more popular, so will be OTT video services.
Traditional cable and satellite services are taking action to face these market changes. As an example, Time Warner has just taken 10% of Hulu stakes, one of the main OTT players.